Risks and Complications of Bunions
Bunions can lead to several complications and increase your risk for developing more serious health issues, even beyond the foot itself.
Bunions can lead to several complications and increase your risk for developing more serious health issues, even beyond the foot itself.
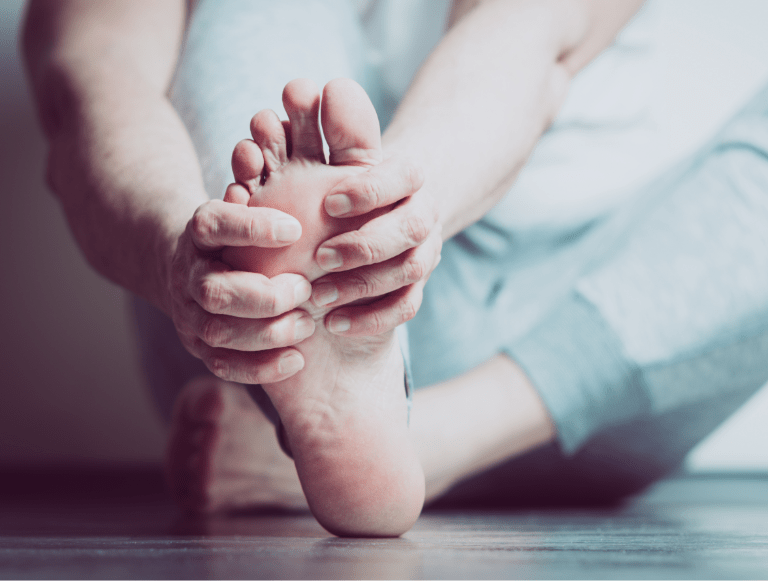


The bunion can also cause the toe to rub against the toe next to it, leading to blisters or calluses where the two toes come in contact with each other (especially if the toes are overlapping). Sores may also form on the point of the bunion protrusion as it is more likely to rub against shoes and become irritated. Similar to calluses, corns are dead skin cells that become hardened like stones over time, leading to pain. Though corns and blisters are relatively minor and easily treatable issues, they will continue to persist without bunion correction treatment.
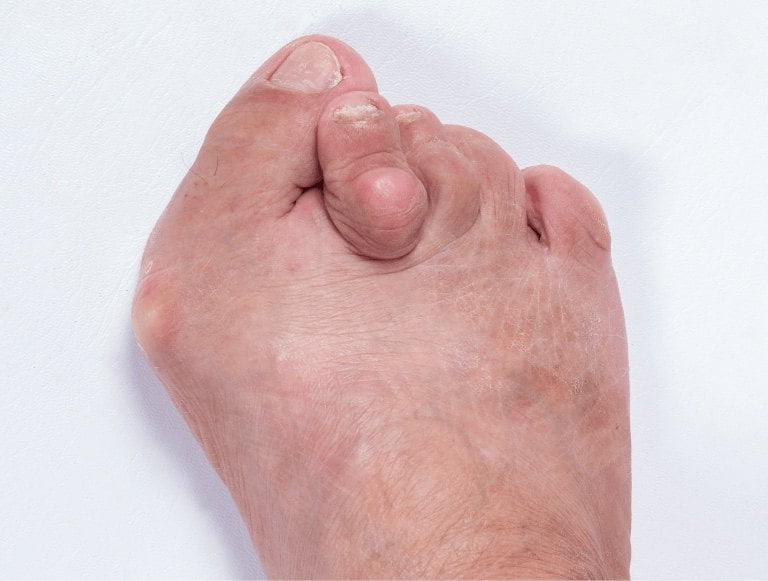
Bursitis is a painful condition that occurs when the small pads around the foot bones, called bursae, become inflamed. These fluid-filled sacs help protect bones and joints, and when they become swollen, it can also damage the cartilage around the joint. This can then potentially lead to arthritis because it indicates that the joints are under constant pressure.
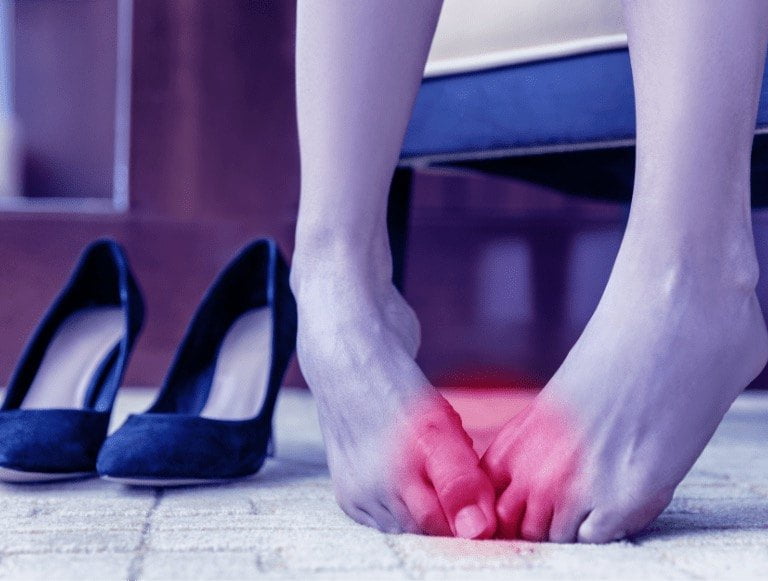

As bunions become swollen, it can affect the soles of your feet and lead to a condition known as Metatarsalgia. Metatarsalgia is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, and it is more common in individuals who frequently run and/or jump. This condition is sometimes caused by a change in the way a person moves and/or supports their weight with different parts of the foot, typically because of the bunion pain itself.
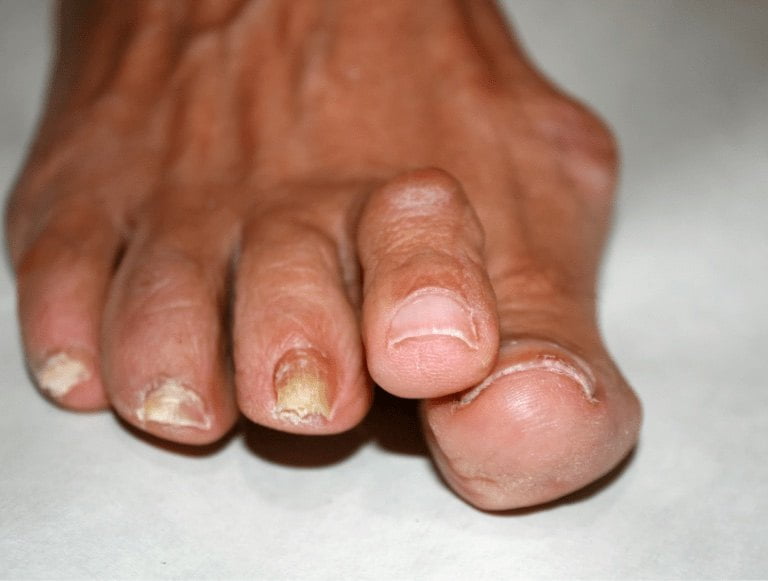
Hammertoe, also referred to as mallet toe, is when any toe becomes bent abnormally at the middle joint, causing the muscles and tendons to become pushed out of position. This can occur when any of the smaller digits bend downward, clawing the ground when a person walks. This occurs due to instability in the foot related to foot misalignment. Hammertoes can form in the toe next to the big toe bunion, but it can also form in any of the smaller toes as bunions might change the way a person walks in response to the pain they are experiencing.
We see bunions in juvenilles commonly at Sydney Bunion Clinic and would encourage that if your child appears to be getting a bunion or has a family history of bunions get it assessed ASAP. This will improve the likelyhood of sucessful conservative management.

People with more severe bunion cases are at a higher risk to develop osteoarthritis, which is degenerative disease results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. When bunions are present, the arthritis is onset by the wear and tear of the affected joints due to poor movement through the joint. Typical osteoarthritis symptoms include joint stiffness, pain, decreased range of motion and swelling.
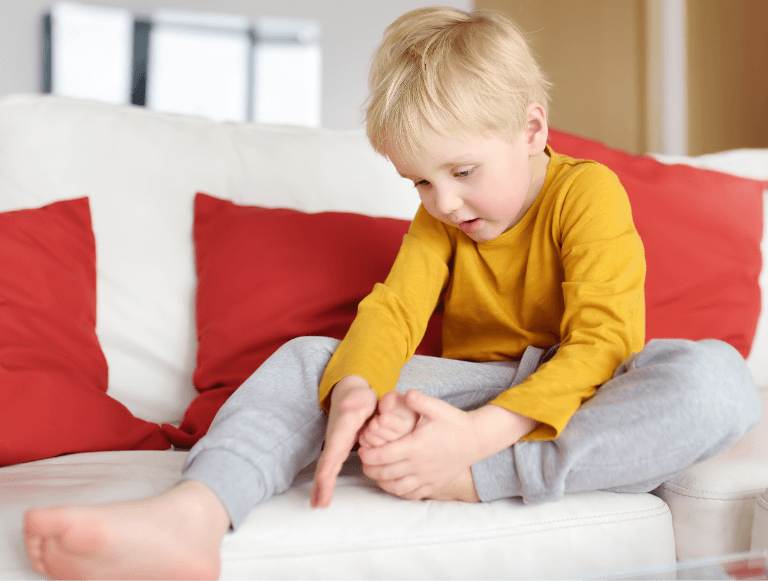

Adolescent bunions are most common in girls between 10 and 15 years old, but boys can also get them. The strongest factor in someone getting a bunion is genetic tendency that is inherited. These inherited traits are stronger on the female side but not always. These traits are the misalignment in the foot that causes compensation that then leads to a bunion.
We see bunions in juvenilles commonly at Sydney Bunion Clinic and would encourage that if your child appears to be getting a bunion or has a family history of bunions get it assessed ASAP. This will improve the likelyhood of sucessful conservative management.
Understanding the Dangers and Complications of Bunion Surgery
Although surgery is usually thought of as the key, it’s important to be notified of the risks of bunion surgery, even if taking bunions may be a challenging experience. Our first concern at Sydney Bunion Clinic is your health and well-being; we provide comprehensive information on what to anticipate should you decide on this treatment course.
Although the complications of bunion surgery might vary, usually, they consist of risks like infection, nerve damage, and the potential of the bunion returning. These side effects of bunion surgery should not be disregarded as they might seriously compromise your general foot condition and recovery.
We know that choosing bunion surgery marks a major decision. For this reason, we are dedicated to informing our patients about all potential results, including bunion surgery problems. Our staff is here to help you navigate your choices so that, given your particular situation, you make the most wise decision.
Let not bunions rule your life. With Sydney Bunion Clinic, know your dangers, investigate your choices, and start your road towards recovery, without the need for painful surgery.

*Claimable on your private health insurance
Sydney Bunion Clinic has successfully treated thousands of bunions in Sydney, we help people avoid bunion surgery through conservative management that is gentle and offers a long term solution.
We provide treatment and care for communities throughout Sydney including Sydney CBD, Fairlight, Queenscliff, Brookvale, North Balgowlah, Chatswood, Drummoyne, Summer Hill, Beaconsfield and Manly from our clinic located in Manly Vale.
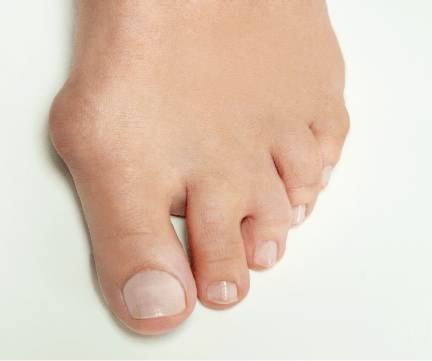
Bunions are a deviation of the big toe where the big toe joint shifts toward the middle of the foot. This can be accompanied by symptoms including pain and a bony growth that turns into a large lump.
Research shows that bunions are extremely prevalent in Australia, affecting ⅓ of the population. Over the age of 60, it’s suggested to be as high as 70%. When left untreated bunions can also be linked to other risks and complications.
Bunions are caused by a number of factors including a family history of bunions, footwear choices and the way you stand and walk, however misalignment of the foot is often the underlying cause.
You may have been told that bunion surgery is the only treatment option available however, there is an non surgical treatment for bunions . We have worked treating bunion without surgery for over 20 years.
Conservative management, such as foot mobilisation, is most effective when treatment of the bunion begins as early as possible, even if the sufferer feels no pain. As a result, often by the time a bunion starts to be painful, significant irreversible damage has already occurred.
Find Relief for Your Bunions Without Surgery
Welcome to Sydney Bunion Clinic, where our goal is to help you find long-lasting bunion pain treatment free of intrusive surgery. Our clinic is aware of the pain and restrictions bunion treatment without surgery may have on your everyday life. Therefore, our area of expertise is, non-invasive methods aimed at the treating the underlying cause of bunions, and avoiding the need for surgical intervention.
Using conservative, corrective treatments, our experienced team provides customized care regimens meant to restore the natural alignment of your foot. We think that bunions should be treated without resorting to invasive bunion surgery; our good experience supports this view. Selecting Sydney Bunion Clinic means you are selecting a more natural, safer approach to treat your bunion without painful surgery. Not to mention a much cheaper option given that bunion surgery can cost over $7500.
Let not bunions rule your life. Accept a future free from suffering and go back to your preferred pastimes confident. Explore Sydney Bunion Clinic to read more about our bunion therapy without surgery and start towards a better, more pleasant life free from the necessity for invasive bunion surgery.
Say farewell to bunions the gentle way; today, see Sydney Bunion Clinic!


What’s the process?
Shop 1, 228 Condamine Street,
Manly Vale NSW 2093

*Claimable on your private health insurance
Sydney Bunion Clinic has successfully treated thousands of bunions in Sydney, we help people avoid bunion surgery through conservative management that is gentle and offers a long term solution.
We provide treatment and care for communities throughout Sydney including Sydney CBD, Fairlight, Queenscliff, Brookvale, North Balgowlah, Chatswood, Drummoyne, Summer Hill, Beaconsfield and Manly from our clinic located in Manly Vale.
Bunions are a deviation of the big toe where the big toe joint shifts toward the middle of the foot. This can be accompanied by symptoms including pain and a bony growth that turns into a large lump.
Research shows that bunions are extremely prevalent in Australia, affecting ⅓ of the population. Over the age of 60, it’s suggested to be as high as 70%. When left untreated bunions can also be linked to other risks and complications.
Bunions are caused by a number of factors including a family history of bunions, footwear choices and the way you stand and walk, however misalignment of the foot is often the underlying cause.
You may have been told that bunion surgery is the only treatment option available however, there is an non surgical treatment for bunions . We have worked treating bunion without surgery for over 20 years.
Conservative management, such as foot mobilisation, is most effective when treatment of the bunion begins as early as possible, even if the sufferer feels no pain. As a result, often by the time a bunion starts to be painful, significant irreversible damage has already occurred.
Find Relief for Your Bunions Without Surgery
Welcome to Sydney Bunion Clinic, where our goal is to help you find long-lasting bunion pain treatment free of intrusive surgery. Our clinic is aware of the pain and restrictions bunion treatment without surgery may have on your everyday life. Therefore, our area of expertise is, non-invasive methods aimed at the treating the underlying cause of bunions, and avoiding the need for surgical intervention.
Using conservative, corrective treatments, our experienced team provides customized care regimens meant to restore the natural alignment of your foot. We think that bunions should be treated without resorting to invasive bunion surgery; our good experience supports this view. Selecting Sydney Bunion Clinic means you are selecting a more natural, safer approach to treat your bunion without painful surgery. Not to mention a much cheaper option given that bunion surgery can cost over $7500.
Let not bunions rule your life. Accept a future free from suffering and go back to your preferred pastimes confident. Explore Sydney Bunion Clinic to read more about our bunion therapy without surgery and start towards a better, more pleasant life free from the necessity for invasive bunion surgery.
Say farewell to bunions the gentle way; today, see Sydney Bunion Clinic!



What’s the process?
Shop 1, 228 Condamine Street,
Manly Vale NSW 2093

*Claimable on your private health insurance